Last updated on February 25th, 2026 at 04:49 am
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) are price imbalances created when the market moves too quickly, leaving inefficiencies.
- They form as a three-candlestick pattern where rapid movement creates a gap between the first and third candles.
- FVGs act as magnets, pulling price back to fill the imbalance and rebalance order flow.
- Not all FVGs are equal; context, timeframe, and alignment with market structure determine their effectiveness.
- FVGs are synonymous with imbalances and liquidity voids but represent specific technical formations.
1. What Does FVG Mean in Trading?
In trading, FVG stands for Fair Value Gap. It refers to a price imbalance or gap that occurs when the market experiences a sharp, aggressive move in one direction. This rapid price action is typically triggered by a significant influx of buy or sell orders, creating areas on the chart where price did not trade efficiently. The concept of FVG is fundamental to price action trading and forms a core pillar of Smart Money Concepts (SMC).
Fair Value Gaps are market inefficiencies. They emerge when buying and selling activities become severely unbalanced, leaving behind price levels that were effectively skipped over. These gaps represent areas where fewer transactions occurred, and as a result, liquidity was left behind. The market, operating algorithmically, has a natural tendency to revisit these areas to fill the imbalance and achieve equilibrium.
2. How Fair Value Gaps Form
Understanding the mechanics of FVG formation is critical to identifying and trading them correctly. An FVG is created through a specific three-candlestick pattern that reveals a gap in price action.
The Three-Candle FVG Pattern
A Fair Value Gap occurs when three consecutive candles form with a large, aggressive move in the middle candle. The gap exists between the high of the first candle and the low of the third candle in a bullish scenario, or between the low of the first candle and the high of the third candle in a bearish scenario.
- Bullish Fair Value Gap: Forms when price moves sharply upward. The gap appears between the high of the first candle and the low of the third candle. The middle candle represents the aggressive buying that created the imbalance.
- Bearish Fair Value Gap: Forms when price drops sharply downward. The gap appears between the low of the first candle and the high of the third candle. The middle candle represents the aggressive selling that created the imbalance.
This three-candle structure is the visual fingerprint of institutional activity. When large players enter the market aggressively, they do not fill every price level along the way. Instead, they create voids in the price action, leaving behind areas that the market will later revisit.
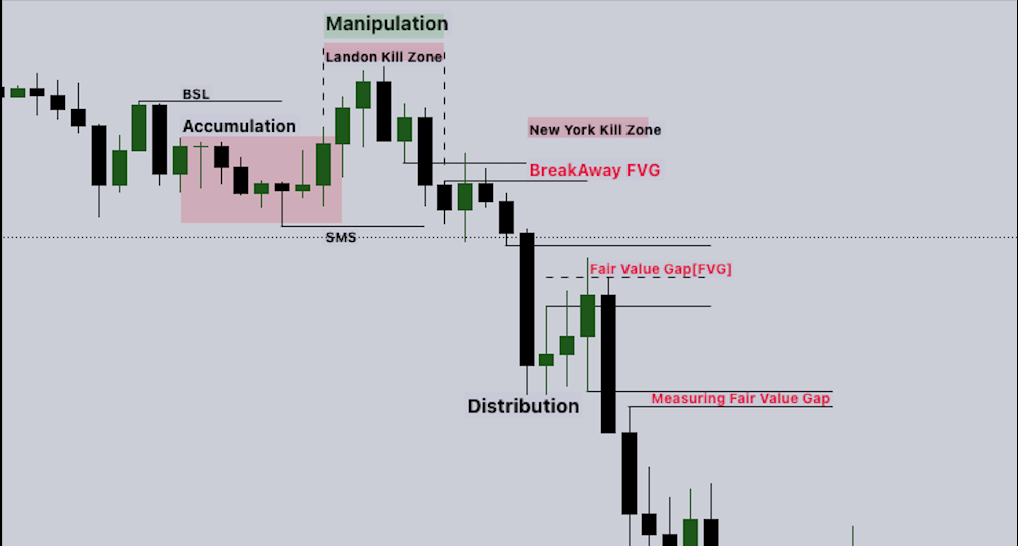
Why FVGs Are Created
Fair Value Gaps are not random. They are the direct result of institutional order flow and algorithmic market behavior. Here are the core reasons FVGs form:
- Imbalance in Order Flow: When the market moves too quickly in one direction, certain price levels do not get traded as much. This creates an imbalance between buyers and sellers at those specific levels.
- Liquidity Hunt: Institutions deliberately create imbalances to trap retail traders and collect liquidity before making their actual move. FVGs are often byproducts of these liquidity sweeps.
- Algorithmic Efficiency: The market operates on algorithms designed to seek and fill inefficiencies. Once an FVG is created, the algorithm flags it as an area requiring rebalancing.
- Urgency in Execution: Large institutional orders are executed with urgency to avoid slippage and front-running. This urgency creates gaps as price leaps from one level to another without proper fill.
3. How Fair Value Gaps Work in the Market
Once a Fair Value Gap has been created, it does not simply disappear. The market has a memory, and unfilled price levels act as magnets, drawing price back to achieve balance. Understanding how FVGs function within the broader market structure is essential for profitable trading.
Price as a Magnet
The Fair Value Gap acts as a target for price to retrace before continuing its trend. The market seeks to revisit areas where liquidity was left behind. This is not a matter of if, but when. The gap will eventually be filled as the market rebalances the order flow that was disrupted during the initial aggressive move.
Think of an FVG as a debt the market owes. The imbalance created during the rapid move must be settled. When price returns to fill the gap, it is effectively paying back that debt by allowing participants who missed the initial move to enter at those levels.
Market Filling the Gap
Over time, the market will fill these gaps, returning to the levels where fewer transactions occurred to balance the order flow. This filling process can happen immediately, within hours, or even days later depending on the timeframe and market conditions. The key principle is that the gap will not be ignored indefinitely.
When price reenters an FVG, one of two things typically happens:
- Continuation: Price fills the gap partially or fully, then continues in the original direction of the impulsive move. This is common when the FVG aligns with the prevailing trend.
- Reversal: Price fills the gap and then reverses direction. This occurs when the FVG is located at a significant structural level or when the original move was a false breakout designed to trap traders.
FVGs and Liquidity
Fair Value Gaps are intrinsically linked to liquidity. The rapid price movement that creates an FVG leaves unfilled orders behind. These unfilled orders represent liquidity that institutions and algorithms will seek to absorb. When price returns to the FVG, it is accessing this liquidity pool, which often triggers a reaction.
Traders who understand this dynamic can position themselves ahead of the crowd. By anticipating the return to the FVG, you gain an edge over those who only react to price movement after it has already occurred.
4. Types of Fair Value Gaps
Not all Fair Value Gaps are created equal. Context, location, and market structure determine the quality and reliability of each FVG. Understanding the different types allows you to filter out low-probability setups and focus on the gaps with the highest chance of success.
Bullish Fair Value Gap
A Bullish FVG forms during an aggressive upward move. The gap appears between the high of the first candle and the low of the third candle. This type of gap suggests that buyers overwhelmed sellers, creating an imbalance to the upside.
| 📈 Bullish FVG | Indicates strong buying pressure. When price retraces into this gap, it often finds support and bounces higher, continuing the uptrend. |
Bearish Fair Value Gap
A Bearish FVG forms during an aggressive downward move. The gap appears between the low of the first candle and the high of the third candle. This type of gap indicates that sellers dominated buyers, creating an imbalance to the downside.
| 📉 Bearish FVG | Indicates strong selling pressure. When price retraces into this gap, it often finds resistance and drops lower, continuing the downtrend. |
Displacement FVGs
Displacement FVGs occur during extremely volatile moves where price makes a sudden, violent shift in direction. These gaps are often larger and more pronounced than standard FVGs. Displacement gaps carry higher significance because they represent a decisive shift in market sentiment and order flow.
These gaps are typically found at the beginning of major trends or following significant news events. They signal that smart money has entered aggressively, and the market structure has fundamentally changed.
5. How to Identify Fair Value Gaps on Your Chart
Identifying Fair Value Gaps is a skill that improves with practice and screen time. The process is straightforward once you understand the visual pattern and the context required for validation.
Step 1: Look for Aggressive Three-Candle Moves
Scan your chart for areas where three consecutive candles form with a sharp, impulsive move in the middle candle. The first and third candles should not overlap in their wicks or bodies, creating a visible gap on the chart.
Step 2: Measure the Gap
The gap is the space between the high of the first candle and the low of the third candle (for bullish FVGs), or between the low of the first candle and the high of the third candle (for bearish FVGs). This space represents the imbalance that will later act as a magnet for price.
Step 3: Confirm the Timeframe
FVGs appear on all timeframes, but not all are equally significant. Higher timeframe FVGs (4-hour, daily, weekly) carry more weight and are more reliable than lower timeframe gaps (1-minute, 5-minute). Focus your attention on gaps formed on higher timeframes for the best probability setups.
Step 4: Check Market Structure
An FVG in isolation is not enough. You must evaluate the broader market structure. Is the gap aligned with the prevailing trend? Does it sit at a key structural level? The most reliable FVGs are those that align with the dominant order flow and occur at significant support or resistance zones.
6. How to Trade Fair Value Gaps Successfully
Trading FVGs requires patience, precision, and proper context. The gap itself is not a signal to enter; it is a zone of interest where you wait for additional confirmation before committing capital.
Step 1: Identify the Trend and Bias
Before trading any FVG, establish the prevailing market trend. Are you in an uptrend, a downtrend, or a range? Your directional bias must align with the type of FVG you are trading. Trading a bullish FVG in a bearish market is low probability and will result in frequent losses.
Step 2: Wait for Price to Return to the Gap
Once you have identified a valid FVG, mark the gap on your chart and wait. Price will eventually return to fill the imbalance. Do not chase price into the gap. Let it come to you. Patience here is mandatory, not optional.
Step 3: Look for Confirmation
When price reenters the FVG zone, drop to a lower timeframe and look for confirmation signals. These can include:
- Rejection candles (pin bars, engulfing patterns)
- Market structure shifts on lower timeframes
- Volume spikes indicating institutional interest
- Confluence with other support or resistance levels
Step 4: Enter the Trade
Once confirmation appears, enter your position. Your entry should be within the FVG zone, ideally at the mean threshold (50% level of the gap) for optimal risk-to-reward.
Step 5: Set Your Stop Loss
For bullish setups, place your stop loss below the low of the FVG. For bearish setups, place your stop loss above the high of the FVG. This ensures that if the gap fails to hold, you are stopped out before significant damage occurs.
Step 6: Take Profit at Key Levels
Set your take-profit target at the next key level of support or resistance, or at a predefined risk-to-reward ratio (minimum 1:2, ideally 1:3 or better). If the move is strong and aligned with a larger trend, consider using a trailing stop to maximize profits.
7. Advanced Fair Value Gap Concepts
FVG Mitigation vs. Invalidation
Understanding the difference between mitigation and invalidation is critical for managing FVG trades effectively.
Mitigation: An FVG is mitigated when price enters the gap and traders or institutions execute their pending orders in that zone. Mitigation happens as the market absorbs the liquidity in the gap. Price usually shows a reaction at this point, either reversing or continuing based on the new balance of buy and sell orders.
Invalidation: An FVG is invalidated when price fills the gap completely and continues moving strongly against your directional bias. Once the gap no longer offers the liquidity imbalance it once did, it loses its predictive power. If the gap contradicts your overall market view, it should be disregarded.
Which Fair Value Gap to Use?
When multiple FVGs appear on a chart, prioritize those that align with institutional order flow and the prevailing market structure. In a bearish setup, focus on FVGs above equilibrium for short entries. In a bullish setup, focus on FVGs below equilibrium for long entries. The key is to combine the FVG with the broader trend direction and market behavior.
How Long Are Fair Value Gaps Valid?
There is no expiration date on Fair Value Gaps. They remain valid indefinitely until price reenters and fills the gap. The market does not care about time in these cases; liquidity is what drives the move. However, relevance may diminish if the gap becomes outdated compared to more current market structures. Fresher FVGs carry more weight than older, unfilled gaps.
Are Fair Value Gaps Always Filled?
Fair Value Gaps are usually filled, but the timing can be uncertain. While price eventually seeks to balance inefficiencies, the market may take longer than expected to revisit these areas. Patience is essential. The underlying reason is that unfilled orders do not expire; they remain valid until the market finds liquidity to rebalance those areas.
8. Fair Value Gap FAQs
Does the Fair Value Gap Work?
Yes, Fair Value Gaps can be extremely effective, but their success largely depends on the trader’s ability to interpret market structure and identify the right conditions. FVGs do not operate in isolation; they require a deep understanding of institutional order flow, liquidity, and context within the overall trend. When used correctly, FVGs provide high-probability trade setups with clear entry and exit criteria.
Is the Fair Value Gap the Same as an Imbalance?
Theoretically, both represent inefficiencies in price, but they are different concepts in practice. FVG is a specific form of imbalance identified within a three-candle pattern, while an imbalance can refer to any price area where trade flow is unbalanced. Visually, FVGs have a clear gap in price action, whereas imbalances may not always form such a distinct pattern. In most trading contexts, the terms are used interchangeably, but FVG is the more precise technical term.
What is the Difference Between FVG and Liquidity Void?
A Liquidity Void is a broader concept that describes any area on the chart where minimal trading occurred due to rapid price movement. An FVG is a specific type of liquidity void defined by the three-candle pattern. All FVGs are liquidity voids, but not all liquidity voids qualify as FVGs. The distinction matters when marking zones on your chart; FVGs provide more precise entry levels, while liquidity voids are larger, less defined areas.
9. Common Mistakes When Trading FVGs
- Trading Against the Trend: One of the most costly mistakes is trading FVGs that oppose the prevailing market structure. Always align your FVG trades with the dominant trend and order flow direction.
- Entering Without Confirmation: Jumping into an FVG zone without waiting for lower-timeframe confirmation leads to premature entries and stopped-out trades. Always wait for rejection patterns or structure shifts.
- Ignoring Higher Timeframes: Lower timeframe FVGs generate more noise and false signals. Focus on 4-hour, daily, and weekly FVGs for the most reliable setups.
- Overtrading Every Gap: Not every FVG deserves a trade. Be selective. Only trade gaps that align with multiple confluences, including trend, structure, and liquidity context.
- Poor Risk Management: Failing to set proper stop losses or taking profits too early destroys the edge that FVGs provide. Stick to your plan and let winners run.
download fair value gap pdf:
Conclusion
Fair Value Gaps are one of the most powerful tools available to price action traders. They reveal the footprints of institutional activity and provide precise zones where the market is likely to react. By understanding how FVGs form, how they function within market structure, and how to trade them with proper confirmation, you gain a significant edge over traders who rely solely on lagging indicators.
The complete formula for FVG trading success is threefold:
- Identification: Find valid gaps formed by three-candle patterns with clear imbalances.
- Context: Trade only the FVGs that align with the prevailing trend and market structure.
- Execution: Enter on lower-timeframe confirmation, set precise stops, and manage risk aggressively.
Master these principles, backtest extensively, and you will develop an intuitive sense for which FVGs offer the highest probability setups. The market leaves clues everywhere. Fair Value Gaps are among the clearest.
