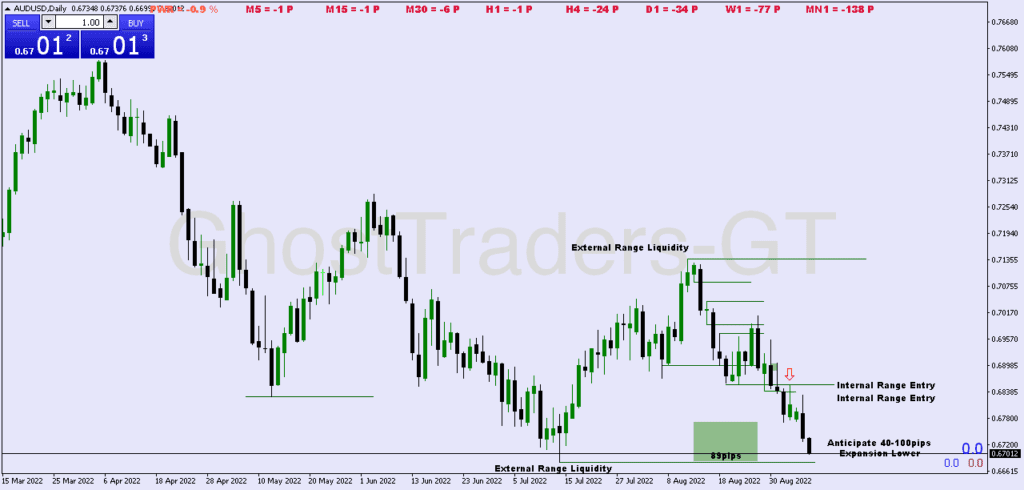
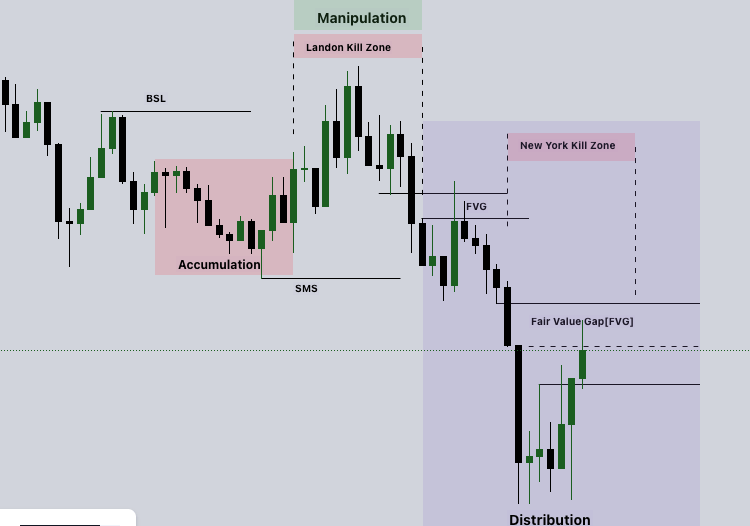
A dealing range is a range-bound area where price oscillates between a defined high and low, often due to institutional order accumulation or distribution. During this phase, institutions accumulate positions quietly without creating large price movements, ensuring they don’t reveal their intentions. The dealing range(DR) acts as a zone of liquidity, which provides the groundwork for breakouts or reversals that drive future trends.
This range can span across multiple sessions, such as the Asian session or pre-London session, serving as a foundation for liquidity hunts when the market becomes active later.
Characteristics of a Dealing Range
- Defined Boundaries (Highs and Lows):
- The dealing range is marked by clear highs and lows, which are important liquidity points. These levels often act as magnets for price when the market begins to move.
- Consolidation Phase:
- During the range, price consolidates, creating sideways movement with low volatility. This signals that institutions are building their positions without causing significant price shifts.
- Liquidity Accumulation:
- Stop-loss orders placed above and below the dealing range become liquidity targets for institutions. These orders fuel the future breakout or reversal moves.
- Session Influence:
- The Asian session frequently establishes dealing ranges, which are tested or broken during the London and New York sessions.
Why Institutions Use Dealing Ranges
- Accumulate or Distribute Positions:
Institutions use dealing ranges to accumulate large orders without triggering volatility. Once they’ve acquired enough liquidity, they push the market in the desired direction. - Create Liquidity Pools:
- Retail traders often place stop-losses just beyond the dealing range, creating liquidity pockets. These pockets give institutions the liquidity needed to execute their trades efficiently during breakouts or reversals.
- Manipulate Retail Traders:
- Institutions use the dealing range to trap retail traders into thinking the market is range-bound, only to trigger stop-hunts when the range is broken.
How to Identify a Dealing Range on the Chart
- Look for Consolidation Zones:
- Identify areas where price oscillates sideways, forming consistent highs and lows. This is often observed during low-volatility sessions, such as the Asian session.
- Mark the Range Boundaries:
- Use horizontal lines to mark the highs and lows of the dealing range. These levels often act as liquidity targets.
- Analyze Volume and Candlestick Behavior:
- During a dealing range, price tends to produce narrow candles with lower volume. The absence of large moves indicates institutional accumulation.
- Watch for Session Breakouts:
- Pay attention to how the market behaves as the London or New York sessions open—these sessions often test or break the dealing range.
How to Trade Dealing Ranges Effectively
Once you’ve identified a dealing range, the next step is to trade it strategically, using smart money trading principles to avoid retail traps. Here are three key strategies to consider.
1. Liquidity Grab and Reversal Setup
The highs and lows of a dealing range act as liquidity zones where stop-losses are accumulated. Institutions often push price beyond these levels to grab liquidity, only to reverse the market in the opposite direction.
How to Trade It:
- Wait for a Liquidity Grab: Allow price to break slightly above or below the dealing range to collect liquidity.
- Enter After the Reversal: Once the liquidity grab is complete, look for price action confirmation (e.g., pin bars or engulfing candles).
- Set Stop-Loss and Target: Place your stop-loss just beyond the liquidity grab and aim for the opposite side of the range as your first target.
2. Trend Continuation After Breakout
Sometimes, the breakout from a dealing range is genuine and signals the start of a new trend. Use this opportunity to trade in the direction of the breakout with a retest entry.
How to Trade It:
- Identify the Breakout: Monitor the London or New York session open for a decisive breakout beyond the dealing range.
- Wait for a Retest: Enter the trade when price pulls back to retest the broken range boundary or order block.
- Manage Risk: Place your stop-loss inside the range, and set your target at the next liquidity pool.
3. Range Play: Scalping the Boundaries
If the dealing range remains intact during the session, you can trade the range boundaries by buying at support and selling at resistance.
How to Trade It:
- Enter at the Range Extremes: Look for opportunities to buy near the range low and sell near the range high.
- Use Tight Stops: Place your stop-loss just beyond the range boundary to manage risk.
- Exit at the Opposite Boundary: Take profit at the opposite end of the range.
Tips for Trading D.Rs with Confidence
- Monitor Session Timing:
- Dealing ranges are often tested or broken during the London and New York sessions. Be patient and align your trades with these active periods.
- Use Higher Timeframe Context:
- Always confirm your range trades by checking the higher timeframe trend—this helps avoid getting caught in false moves.
- Watch for False Breakouts:
- Many breakouts are engineered to trap retail traders. Always wait for confirmation or a retest before entering trades.
- Manage Risk Carefully:
- Use tight stop-losses when trading within a dealing range to minimize exposure during volatile market shifts.
Conclusion
A dealing range is a crucial tool for identifying institutional activity and aligning your trades with smart money movements. Recognizing these ranges and understanding how institutions accumulate or distribute liquidity within them allows traders to anticipate breakouts, reversals, and liquidity grabs.
By using strategies such as liquidity grabs, range plays, and breakout retests, traders can capitalize on the opportunities dealing ranges provide. Patience, discipline, and session timing are essential to succeeding with these setups. With practice, mastering the dynamics of dealing ranges will enhance your ability to trade with precision and confidence in alignment with institutional flows.