What is the fair value gap in forex?
A Fair Value Gap (FVG) in Forex trading is when the price of a currency pair leaves a specific level where there’s less trading activity seen and only has a one-directional price movement. Fvg can present new trading opportunities especially when coupled with order blocks.
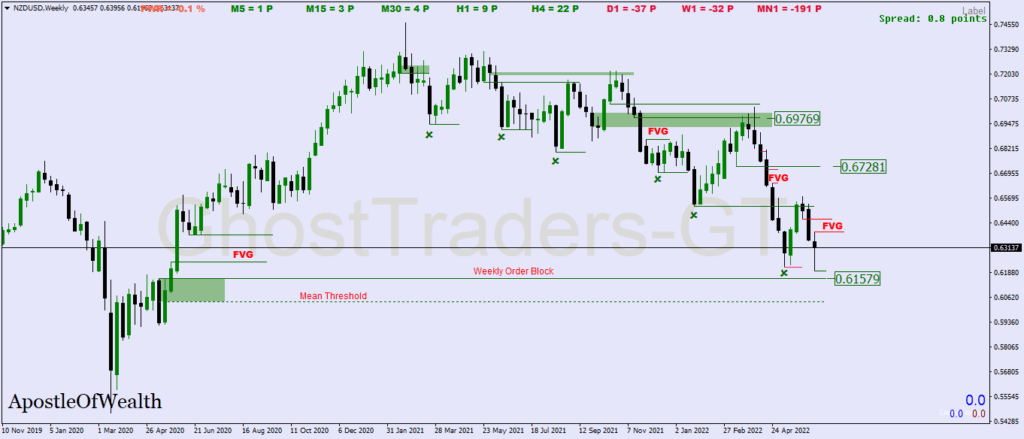
From The Chart Example, we can see how price declined significantly after closing our fair value gap, based on the order flow being bearish we can say this is a bearish fair value gap.
Price is most likely to reach out to areas where there are Fvg and Liquidity voids. The understanding of order flow trading should be coupled with fvg and liquidity void in order to select the best fair value gaps and liquidity voids.
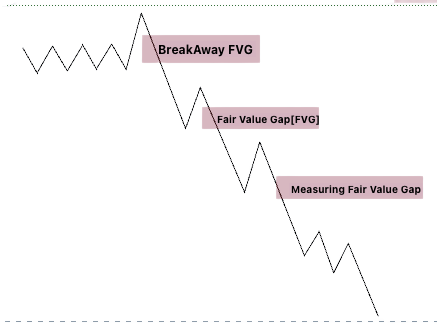
Breakaway Fair Value Gap
A Breakaway Fair Value Gap is a significant price gap in the market that occurs when the price breaks out of a consolidation phase or trading range. This is a crucial concept used by experienced traders, such as GhostTraders, to gauge the strength of a trend and identify potential trading opportunities.
These gaps can manifest in both bullish and bearish markets and are characterized by a sudden surge in trading volume. This surge indicates a profound shift in market sentiment and direction.
In a Bullish Breakaway Gap, the price breaks above a resistance level, signaling that buyers have gained control of the market.
Conversely, in a Bearish Breakaway Gap, the price breaks below a support level, indicating that sellers have taken control.
Breakaway gaps often remain open for a crucial reason – they represent a rapid and substantial change in market sentiment and momentum. When a breakaway gap occurs, it signifies a shift in the balance between buyers and sellers. Consequently, there might be limited trading activity at the price level where the gap occurred, causing the gap to persist.
This lack of activity can persist until a substantial volume of buying or selling activity intervenes, either propelling the price higher or lower and causing the gap to close. The reason behind these gaps remaining open lies in the hesitancy of traders. Those who held positions at the gap level may be looking to sell to cut losses, while new traders may view it as too risky to buy at that level.
In essence, breakaway gaps are a powerful signal of changing market dynamics, and their persistence is a reflection of the uncertainty and caution among traders during these pivotal moments in the market.
Measuring Fair Value Gap
In addition to Breakaway Gaps, there’s another crucial concept known as the “Measuring Fair Value Gap” in the world of Forex trading. It’s formed following a Fair Value Gap and plays a unique role in analyzing market dynamics.
The Measuring Fair Value Gap is characterized by its propensity to remain open. This persistence occurs because heavy institutional order flow often surrounds it, pushing prices consistently in one direction. As a result, the Measuring Gap is less likely to be closed. Its primary purpose is to act as an indicator of institutional order flow in a specific direction.
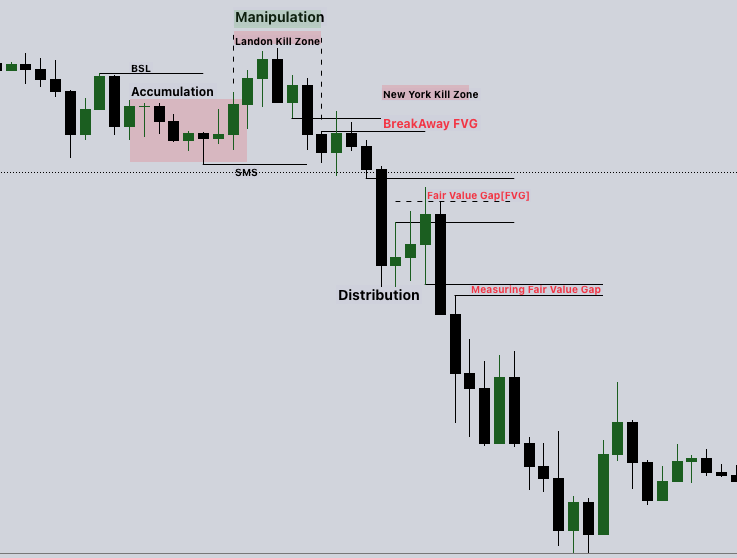
When a Bearish Measuring Fair Value Gap appears, it signals a dominant bearish order flow in the market. Conversely, a Bullish Measuring Gap indicates a prevailing bullish order flow.
The key reason behind the Measuring Gap’s tendency to remain open lies in the substantial institutional order flow that accompanies it. Institutions often execute large orders that drive the market decisively in a single direction, leaving little room for price retracement.
In summary, the Measuring Fair Value Gap serves as a valuable tool for traders to identify and interpret institutional order flow. Its persistence and direction provide valuable insights into the prevailing market sentiment, assisting traders in making informed decisions.
consequent encroachment forex
Consequent encroachment(CE) is when a fair value gap is filled by 50%, this is what is referred to as the mean threshold of fvg. Traders should keep in mind that price might not fill the fvg. therefore targeting the mean threshold is ideal not to miss trades.
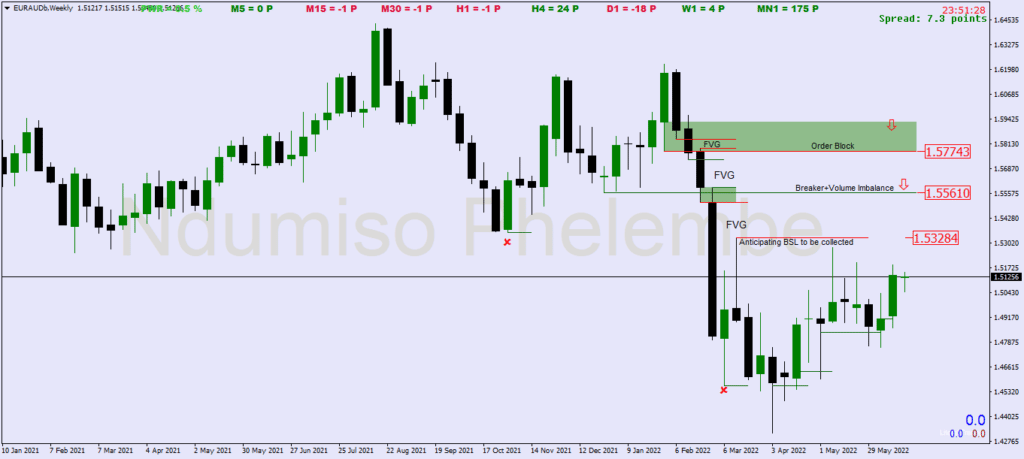
Liquidity Voids
Liquidity voids occur when price moves sharply in one direction. This is portrayed by large candles that have little trading activity as price moves in one direction. Eventually, the price will return to close the liquidity void later.

The Right Fair Value Gap to Trade
To identify the ideal bearish fair value gap, check for the fvg at the premium level or above the discount of the defined range using Fibonacci Levels. Similarly, to identify a bullish fair value gap, look for fvg below the discount level of your defined range using Fibonacci Levels.
Institutional order flow entry drill (IOFED)
Institutional Order Flow Entry Drill(IOFED) occurs when price fills less than 50% of a Fair Value Gap(FVG), unlike consequence encroachment when the price is 50% of a Fair Value Gap(FVG).In the chart below you can see how prices filled less than 50% of fair value and declined significantly.
The understanding of institutional order flow entry drills and consequence encroachment allows traders to understand that prices might not fill fair value gaps due to heavy order flow pushing prices up or down rapidly before they fill an FVG. Your FVG entry should be based on these concepts to ensure you don’t miss a trade.

Fair value gap and order block
As defined before in this article titled: Best Order Block Trading Guide An Order Block(OB) in forex is a change in the state of price delivery indicated by the last up or last down close candle with a fair value gap as an order block validator. whilst a fair value gap is a price gap that indicates buy-side inefficiency(sell-side imbalance) or sell-side inefficiency(buy-side imbalance) in the market.

Similarities and Differences between Fair Value Gap and Liquidity Void
Fair value gaps and liquidity voids are both indicators of sell-side imbalance and buy-side imbalance in trading. The only difference is how they are represented in the forex trading chart, as stated in this blog titled: Fair Value Gaps and Liquidity Void Guide, Liquidity voids occur when price moves sharply in one direction forming long-range candles. whilst a fair value is a price gap.
| Fair Value Gap | Liquidity Void |
|---|---|
| Price gap | Long-range candles |
| Indicates sell-side and buy-side imbalance | Indicates sell-side and buy-side imbalance |
| Represented differently on Forex trading chart | Represented differently on the Forex trading chart |
Fair Valu Gap Trading | How To Trade Fair Value Gaps|Fair Value Gap Trading Strategy
When price collects sell-side or buy-side liquidity we anticipate either a reversal, retracement, or continuation. in this case of fair value gap trading, our main focus is trading reversal using a fair value gap as our entry point.

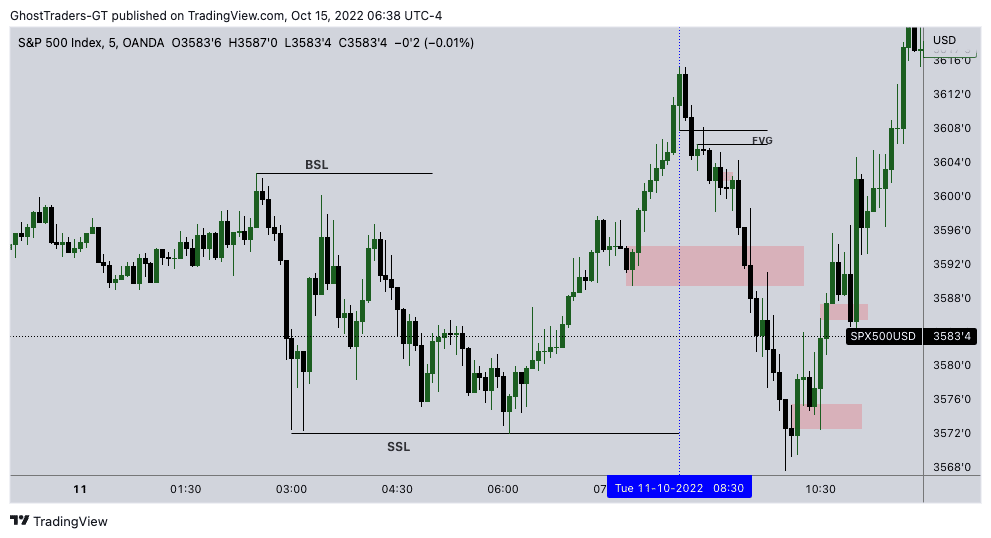
Sell Setup Trading
When Price Collects buy-side Liquidity(BSL) we anticipate a reversal. wait for a shift in market structure to confirm the anticipated reversal, once we have a shift in market structure look for a fair value gap and use it as an entry point to sell short.

Buy Setup Trading
When Price Collects Sell Side Liquidity(BSL) we anticipate a reversal. wait for a shift in market structure to confirm the anticipated reversal. once we have a shift in market structure look for a fair value gap and use it as an entry point to buy or enter a long position.
The institutional reference points for this trading model are fair value Gap, Shift in Market Structure, sell-side liquidity (SSL), and Buy-Side liquidity (BSL).
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the meaning of a Fair Value Gap in trading?
In Theory, A Fair Value Gap is the difference between the current market price of a financial instrument and its fair value. Fair value is the estimated worth of an asset based on its underlying fundamental factors such as earnings, dividends, and interest rates. Fair Value Gap trading strategy involves buying or selling an asset when the market price deviates significantly from its fair value.
How can one identify a Fair Value Gap on trading charts?
Traders can identify a Fair Value Gap by comparing the current market price of an asset with its fair value. They can use various technical indicators such as moving averages, trend lines, and oscillators to determine the fair value of an asset. A significant deviation from the fair value can indicate a potential trading opportunity.
What strategies are most effective for trading Fair Value Gaps?
The most effective strategy for trading Fair Value Gaps is to buy or sell an asset when the market price deviates significantly from its fair value. Traders can use various technical indicators to identify potential trading opportunities and set stop-loss orders to manage their risk. Additionally, traders can use fundamental analysis to determine the fair value of an asset and compare it with the current market price.
Can trading with Fair Value Gaps be consistently profitable, and what are the risks?
Trading with Fair Value Gaps can be consistently profitable if traders have a sound trading strategy and manage their risk effectively. However, like any other trading strategy, Fair Value Gap trading carries risks such as market volatility, liquidity risk, and execution risk. Traders should always use stop-loss orders and never risk more than they can afford to lose.
How does an Order Block relate to a Fair Value Gap in trading?
An Order Block is a price level where a significant number of buy or sell orders are placed, creating a potential support or resistance level. Order Blocks can be used to identify potential Fair Value Gaps as they can indicate where the market price may deviate significantly from the fair value. Traders can use Order Blocks to set their entry and exit points and manage their risk effectively.
Learn More From Our Popular Courses:
Hey Check Our Instagram account and stay updated.





